这篇文章主要是从源码的级别来看Raft算法的实现。在网上找到了一个简化版:源码.
一个Server结构代表Raft网络中的一个节点。节点会创建一个Server,并且通过端(peers)接口的方式暴露给其他节点。
传输层采用http包装,端对端通信通过rest http方式。
|http transport| ---> |peers| ---> |server|
项目简介
节点的增加和删除
支持动态增删节点,采用一个简单的共识算法(节点更新时,接受配置更新的节点需要超过1/2,即新集群要大于旧集群)。
roadmap
- leader选举
- 日志复制
- 单元测试
- http 传输层
- 配置变更
除此之外,还有一些是未完成的
- net/rpc 传输层或者其他类型的传输层
- 日志压缩
- 快照安装以及恢复
- 完整的demo应用
- 一些比较复杂的测试用例
具体细节,看下面的代码分析。
源码分析
源码目录结构
├── JOINT-CONSENSUS.md
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── configuration.go // 配置
├── example_test.go // demo
├── log.go // 日志
├── log_test.go // 日志测试模块
├── peers.go // 端
├── peers_test.go // 端模块
├── rpc.go // rpc 对象模块
├── server.go // server模块
├── server_internals_test.go // server内部测试模块
├── server_test.go // server测试模块
├── transport.go // 传输层
└── transport_test.go // 传输层模块
主要的数据结构
rpc.go
// 日志追加
type appendEntriesTuple struct {
// 日志追加请求
Request appendEntries
// 应答通道
Response chan appendEntriesResponse
}
// 投票选举
type requestVoteTuple struct {
// 选举内容
Request requestVote
// 选举结构应答
Response chan requestVoteResponse
}
// appendEntries represents an appendEntries RPC.
// 日志追加-实体
type appendEntries struct {
// 任期号
Term uint64 `json:"term"`
// leader 标识
LeaderID uint64 `json:"leader_id"`
// 前一个日志索引
PrevLogIndex uint64 `json:"prev_log_index"`
// 前一个日志任期号
PrevLogTerm uint64 `json:"prev_log_term"`
// 要追加的实体数组-支持批量追加
Entries []logEntry `json:"entries"`
// 已经committed的缩影
CommitIndex uint64 `json:"commit_index"`
}
// appendEntriesResponse represents the response to an appendEntries RPC.
// 日志追加应答
type appendEntriesResponse struct {
// 应答节点的任期号
Term uint64 `json:"term"`
// 是否追加成功
Success bool `json:"success"`
// 失败的原因
reason string
}
// requestVote represents a requestVote RPC.
// 投票请求实体
type requestVote struct {
// 发起者的任期号
Term uint64 `json:"term"`
// 发起者的id
CandidateID uint64 `json:"candidate_id"`
// 发起者的最新条目
LastLogIndex uint64 `json:"last_log_index"`
// 发起者的最新任期号
LastLogTerm uint64 `json:"last_log_term"`
}
// requestVoteResponse represents the response to a requestVote RPC.
// 投票应答
type requestVoteResponse struct {
// 应答者任期号
Term uint64 `json:"term"`
// 应答结果,true赞同,false反对
VoteGranted bool `json:"vote_granted"`
// 反对原因
reason string
}
log.go
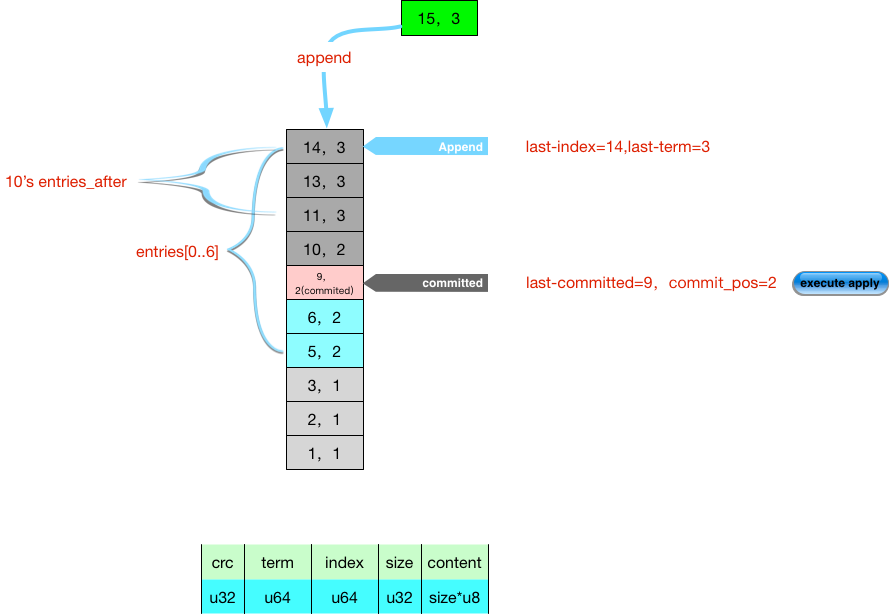
var (
// 任期号太小
errTermTooSmall = errors.New("term too small")
// 日志索引太小
errIndexTooSmall = errors.New("index too small")
// 日志缩影太大
errIndexTooBig = errors.New("commit index too big")
// 日志条目内容已损坏
errInvalidChecksum = errors.New("invalid checksum")
// 无效的命令
errNoCommand = errors.New("no command")
// 错误的日志索引
errBadIndex = errors.New("bad index")
// 错误任期号
errBadTerm = errors.New("bad term")
)
// 日志结构
type raftLog struct {
// 日志读写锁
sync.RWMutex
// 日志存储接口
store io.Writer
// 日志镜像,现在存储于内存
entries []logEntry
// 下一条日志commit索引
commitPos int
// "操作"的回调函数,这个函数比较重要,可以"操作集合"镜像,
// 在快照时,只需要将"结果"快到存储层即可
apply func(uint64, []byte) []byte
}
func newRaftLog(store io.ReadWriter, apply func(uint64, []byte) []byte) *raftLog {
l := &raftLog{
store: store,
entries: []logEntry{},
commitPos: -1, // no commits to begin with
apply: apply,
}
l.recover(store)
return l
}
// recover reads from the log's store, to populate the log with log entries
// from persistent storage. It should be called once, at log instantiation.
// 日志恢复,当服务重启时,重建日志条目(一般重建都是居于于快照和日志的,可是这里没有实现快照,所以从日志中重建即可)
// 1、这里的日志时commited之后的日志,所以重建时,commitPos也会更新
// 2、重建日志条目,会调用apply函数,对日志进行处理,这个函数相当于"状态机"功能;如果有快照(相当于Redis 的RDB),先将安装快照,再恢复日志(相当于Redis 的aof)
func (l *raftLog) recover(r io.Reader) error {
for {
var entry logEntry
switch err := entry.decode(r); err {
case io.EOF:
return nil // successful completion
case nil:
if err := l.appendEntry(entry); err != nil {
return err
}
l.commitPos++
l.apply(entry.Index, entry.Command)
default:
return err // unsuccessful completion
}
}
}
// entriesAfter returns a slice of log entries after (i.e. not including) the
// passed index, and the term of the log entry specified by index, as a
// convenience to the caller. (This function is only used by a leader attempting
// to flush log entries to its followers.)
//
// This function is called to populate an AppendEntries RPC. That implies they
// are destined for a follower, which implies the application of the commands
// should have the response thrown away, which implies we shouldn't pass a
// commandResponse channel (see: commitTo implementation). In the normal case,
// the raftLogEntries we return here will get serialized as they pass thru their
// transport, and lose their commandResponse channel anyway. But in the case of
// a LocalPeer (or equivalent) this doesn't happen. So, we must make sure to
// proactively strip commandResponse channels.
// 检索index之后的日志条目
func (l *raftLog) entriesAfter(index uint64) ([]logEntry, uint64) {
l.RLock()
defer l.RUnlock()
// 1.检索出index对应term以及在实体集合entries中的位置Pos
pos := 0
lastTerm := uint64(0)
for ; pos < len(l.entries); pos++ {
if l.entries[pos].Index > index {
break
}
lastTerm = l.entries[pos].Term
}
a := l.entries[pos:]
if len(a) == 0 {
return []logEntry{}, lastTerm
}
// 除去command Response channel
return stripResponseChannels(a), lastTerm
}
func stripResponseChannels(a []logEntry) []logEntry {
stripped := make([]logEntry, len(a))
for i, entry := range a {
stripped[i] = logEntry{
Index: entry.Index,
Term: entry.Term,
Command: entry.Command,
commandResponse: nil,
}
}
return stripped
}
// contains returns true if a log entry with the given index and term exists in
// the log.
// 判断是够包含{term, index}条目
func (l *raftLog) contains(index, term uint64) bool {
l.RLock()
defer l.RUnlock()
// It's not necessarily true that l.entries[i] has index == i.
for _, entry := range l.entries {
if entry.Index == index && entry.Term == term {
return true
}
if entry.Index > index || entry.Term > term {
break
}
}
return false
}
// 判断{term, index}是否为最新的日志条目,如果是,则将则将在其之后的日志清理掉,
// 这个条目应该在[commit_index, last_index]范围内
func (l *raftLog) ensureLastIs(index, term uint64) error {
l.Lock()
defer l.Unlock()
// Taken loosely from benbjohnson's impl
if index < l.getCommitIndexWithLock() {
return errIndexTooSmall
}
if index > l.lastIndexWithLock() {
return errIndexTooBig
}
// It's possible that the passed index is 0. It means the leader has come to
// decide we need a complete log rebuild. Of course, that's only valid if we
// haven't committed anything, so this check comes after that one.
// 全部重建,前提是没有commited过任何的条目
if index == 0 {
for pos := 0; pos < len(l.entries); pos++ {
if l.entries[pos].commandResponse != nil {
close(l.entries[pos].commandResponse)
l.entries[pos].commandResponse = nil
}
if l.entries[pos].committed != nil {
l.entries[pos].committed <- false
close(l.entries[pos].committed)
l.entries[pos].committed = nil
}
}
l.entries = []logEntry{}
return nil
}
// Normal case: find the position of the matching log entry.
pos := 0
for ; pos < len(l.entries); pos++ {
if l.entries[pos].Index < index {
continue // didn't find it yet
}
if l.entries[pos].Index > index {
return errBadIndex // somehow went past it
}
if l.entries[pos].Index != index {
panic("not <, not >, but somehow !=")
}
if l.entries[pos].Term != term {
return errBadTerm
}
break // good
}
// Sanity check.
// ? 怎么可能出现这种情况?
if pos < l.commitPos {
panic("index >= commitIndex, but pos < commitPos")
}
// `pos` is the position of log entry matching index and term.
// We want to truncate everything after that.
// 应为{term, index}是最新的了,所以将在其之后的所有条目给cut掉
truncateFrom := pos + 1
if truncateFrom >= len(l.entries) {
return nil // nothing to truncate
}
// If we blow away log entries that haven't yet sent responses to clients,
// signal the clients to stop waiting, by closing the channel without a
// response value.
for pos = truncateFrom; pos < len(l.entries); pos++ {
if l.entries[pos].commandResponse != nil {
close(l.entries[pos].commandResponse)
l.entries[pos].commandResponse = nil
}
if l.entries[pos].committed != nil {
l.entries[pos].committed <- false
close(l.entries[pos].committed)
l.entries[pos].committed = nil
}
}
// Truncate the log.
l.entries = l.entries[:truncateFrom]
// Done.
return nil
}
// getCommitIndex returns the commit index of the log. That is, the index of the
// last log entry which can be considered committed.
// 获取最新的commited日志条目
func (l *raftLog) getCommitIndex() uint64 {
l.RLock()
defer l.RUnlock()
return l.getCommitIndexWithLock()
}
// 获取最新的日志条目
func (l *raftLog) getCommitIndexWithLock() uint64 {
if l.commitPos < 0 {
return 0
}
if l.commitPos >= len(l.entries) {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("commitPos %d > len(l.entries) %d; bad bookkeeping in raftLog", l.commitPos, len(l.entries)))
}
return l.entries[l.commitPos].Index
}
// lastIndex returns the index of the most recent log entry.
func (l *raftLog) lastIndex() uint64 {
l.RLock()
defer l.RUnlock()
return l.lastIndexWithLock()
}
func (l *raftLog) lastIndexWithLock() uint64 {
if len(l.entries) <= 0 {
return 0
}
return l.entries[len(l.entries)-1].Index
}
// lastTerm returns the term of the most recent log entry.
func (l *raftLog) lastTerm() uint64 {
l.RLock()
defer l.RUnlock()
return l.lastTermWithLock()
}
func (l *raftLog) lastTermWithLock() uint64 {
if len(l.entries) <= 0 {
return 0
}
return l.entries[len(l.entries)-1].Term
}
// appendEntry appends the passed log entry to the log. It will return an error
// if the entry's term is smaller than the log's most recent term, or if the
// entry's index is too small relative to the log's most recent entry.
// 追加日志,注意此时还没有commit该条目
func (l *raftLog) appendEntry(entry logEntry) error {
l.Lock()
defer l.Unlock()
// 判定{entry.term, entry.index} > {last_term, last_index}
if len(l.entries) > 0 {
lastTerm := l.lastTermWithLock()
if entry.Term < lastTerm {
return errTermTooSmall
}
lastIndex := l.lastIndexWithLock()
if entry.Term == lastTerm && entry.Index <= lastIndex {
return errIndexTooSmall
}
}
l.entries = append(l.entries, entry)
return nil
}
// commitTo commits all log entries up to and including the passed commitIndex.
// Commit means: synchronize the log entry to persistent storage, and call the
// state machine apply function for the log entry's command.
// 注意:
// 1、commit是一个后端任务,再此并没有"1/2"确认的概念(实际上是不是这样呢,这得去参考raft的论文了)
// 2、apply函数是在commit过程中调用,而不是在append的时候调用
// 3、apply相当于状态机函数,一般用户会将这些操作结果保存起来,用于快照
// 比如,想实现一个kv存储,那么用户只要将kv相关的逻辑植入这个函数即可
// committed <= commitIndex <= last_index
func (l *raftLog) commitTo(commitIndex uint64) error {
if commitIndex == 0 {
panic("commitTo(0)")
}
l.Lock()
defer l.Unlock()
// Reject old commit indexes
if commitIndex < l.getCommitIndexWithLock() {
return errIndexTooSmall
}
// Reject new commit indexes
if commitIndex > l.lastIndexWithLock() {
return errIndexTooBig
}
// If we've already committed to the commitIndex, great!
if commitIndex == l.getCommitIndexWithLock() {
return nil
}
// We should start committing at precisely the last commitPos + 1
pos := l.commitPos + 1
if pos < 0 {
panic("pending commit pos < 0")
}
// Commit entries between our existing commit index and the passed index.
// Remember to include the passed index.
for {
// Sanity checks. TODO replace with plain `for` when this is stable.
if pos >= len(l.entries) {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("commitTo pos=%d advanced past all log entries (%d)", pos, len(l.entries)))
}
if l.entries[pos].Index > commitIndex {
panic("commitTo advanced past the desired commitIndex")
}
// Encode the entry to persistent storage.
if err := l.entries[pos].encode(l.store); err != nil {
return err
}
// Forward non-configuration commands to the state machine.
// Send the responses to the waiting client, if applicable.
// 如果不是配置类型的Log,则调用apply function
// 配置类型的Log,在其他地方处理
if !l.entries[pos].isConfiguration {
resp := l.apply(l.entries[pos].Index, l.entries[pos].Command)
if l.entries[pos].commandResponse != nil {
select {
case l.entries[pos].commandResponse <- resp:
break
// 问什么选取这个时间???
case <-time.After(maximumElectionTimeout()): // << ElectionInterval
panic("uncoöperative command response receiver")
}
close(l.entries[pos].commandResponse)
l.entries[pos].commandResponse = nil
}
}
// Signal the entry has been committed, if applicable.
if l.entries[pos].committed != nil {
l.entries[pos].committed <- true
close(l.entries[pos].committed)
l.entries[pos].committed = nil
}
// Mark our commit position cursor.
l.commitPos = pos
// If that was the last one, we're done.
if l.entries[pos].Index == commitIndex {
break
}
if l.entries[pos].Index > commitIndex {
panic(fmt.Sprintf(
"current entry Index %d is beyond our desired commitIndex %d",
l.entries[pos].Index,
commitIndex,
))
}
// Otherwise, advance!
pos++
}
// Done.
return nil
}
// logEntry is the atomic unit being managed by the distributed log. A log entry
// always has an index (monotonically increasing), a term in which the Raft
// network leader first sees the entry, and a command. The command is what gets
// executed against the node state machine when the log entry is successfully
// replicated.
type logEntry struct {
// 日志索引号
Index uint64 `json:"index"`
// 任期号
Term uint64 `json:"term"` // when received by leader
// 日志内容
Command []byte `json:"command,omitempty"`
// commited 通道
committed chan bool `json:"-"`
// 命令应答 通道
commandResponse chan<- []byte `json:"-"` // only non-nil on receiver's log
// 日志类型标示
isConfiguration bool `json:"-"` // for configuration change entries
}
// encode serializes the log entry to the passed io.Writer.
//
// Entries are serialized in a simple binary format:
//
// ---------------------------------------------
// | uint32 | uint64 | uint64 | uint32 | []byte |
// ---------------------------------------------
// | CRC | TERM | INDEX | SIZE | COMMAND |
// ---------------------------------------------
//
// 序列化,大端
func (e *logEntry) encode(w io.Writer) error {
if len(e.Command) <= 0 {
return errNoCommand
}
if e.Index <= 0 {
return errBadIndex
}
if e.Term <= 0 {
return errBadTerm
}
commandSize := len(e.Command)
buf := make([]byte, 24+commandSize)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(buf[4:12], e.Term)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(buf[12:20], e.Index)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(buf[20:24], uint32(commandSize))
copy(buf[24:], e.Command)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(
buf[0:4],
crc32.ChecksumIEEE(buf[4:]),
)
_, err := w.Write(buf)
return err
}
// 反序列化
// decode deserializes one log entry from the passed io.Reader.
func (e *logEntry) decode(r io.Reader) error {
header := make([]byte, 24)
if _, err := r.Read(header); err != nil {
return err
}
command := make([]byte, binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(header[20:24]))
if _, err := r.Read(command); err != nil {
return err
}
crc := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(header[:4])
check := crc32.NewIEEE()
check.Write(header[4:])
check.Write(command)
if crc != check.Sum32() {
return errInvalidChecksum
}
e.Term = binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(header[4:12])
e.Index = binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(header[12:20])
e.Command = command
return nil
}
Peers.go
var (
errTimeout = errors.New("timeout")
)
// peers为节点的一个抽象,对外提供了一些访问接口,
// 需要注意的地方是peers的序列化
type Peer interface {
// 返回server标示
id() uint64
// 日志追加接口
callAppendEntries(appendEntries) appendEntriesResponse
// 投票选举接口
callRequestVote(requestVote) requestVoteResponse
// 命令调用
callCommand([]byte, chan<- []byte) error
// 集群配置变化接口
callSetConfiguration(...Peer) error
}
// localPeer is the simplest kind of peer, mapped to a server in the
// same process-space. Useful for testing and demonstration; not so
// useful for networks of independent processes.
// 本地local peers,用于测试,不用经过网络
type localPeer struct {
server *Server
}
func newLocalPeer(server *Server) *localPeer { return &localPeer{server} }
func (p *localPeer) id() uint64 { return p.server.id }
// 追加日志
func (p *localPeer) callAppendEntries(ae appendEntries) appendEntriesResponse {
return p.server.appendEntries(ae)
}
// 投票选举
func (p *localPeer) callRequestVote(rv requestVote) requestVoteResponse {
return p.server.requestVote(rv)
}
// 命令
// 实际调用为Leader
func (p *localPeer) callCommand(cmd []byte, response chan<- []byte) error {
return p.server.Command(cmd, response)
}
// 设置配置
func (p *localPeer) callSetConfiguration(peers ...Peer) error {
return p.server.SetConfiguration(peers...)
}
// requestVoteTimeout issues the requestVote to the given peer.
// If no response is received before timeout, an error is returned.
// 投票
func requestVoteTimeout(p Peer, rv requestVote, timeout time.Duration) (requestVoteResponse, error) {
c := make(chan requestVoteResponse, 1)
go func() { c <- p.callRequestVote(rv) }()
select {
case resp := <-c:
return resp, nil
case <-time.After(timeout):
return requestVoteResponse{}, errTimeout
}
}
// peerMap is a collection of Peer interfaces. It provides some convenience
// functions for actions that should apply to multiple Peers.
type peerMap map[uint64]Peer
// makePeerMap constructs a peerMap from a list of peers.
func makePeerMap(peers ...Peer) peerMap {
pm := peerMap{}
for _, peer := range peers {
pm[peer.id()] = peer
}
return pm
}
// explodePeerMap converts a peerMap into a slice of peers.
func explodePeerMap(pm peerMap) []Peer {
a := []Peer{}
for _, peer := range pm {
a = append(a, peer)
}
return a
}
func (pm peerMap) except(id uint64) peerMap {
except := peerMap{}
for id0, peer := range pm {
if id0 == id {
continue
}
except[id0] = peer
}
return except
}
func (pm peerMap) count() int { return len(pm) }
// 法定人数
func (pm peerMap) quorum() int {
switch n := len(pm); n {
case 0, 1:
return 1
default:
return (n / 2) + 1
}
}
// requestVotes sends the passed requestVote RPC to every peer in Peers. It
// forwards responses along the returned requestVoteResponse channel. It makes
// the RPCs with a timeout of BroadcastInterval * 2 (chosen arbitrarily). Peers
// that don't respond within the timeout are retried forever. The retry loop
// stops only when all peers have responded, or a Cancel signal is sent via the
// returned canceler.
func (pm peerMap) requestVotes(r requestVote) (chan voteResponseTuple, canceler) {
// "[A server entering the candidate stage] issues requestVote RPCs in
// parallel to each of the other servers in the cluster. If the candidate
// receives no response for an RPC, it reissues the RPC repeatedly until a
// response arrives or the election concludes."
// construct the channels we'll return
abortChan := make(chan struct{})
tupleChan := make(chan voteResponseTuple)
go func() {
// We loop until all Peers have given us a response.
// Track which Peers have responded.
respondedAlready := peerMap{} // none yet
for {
notYetResponded := disjoint(pm, respondedAlready)
if len(notYetResponded) <= 0 {
return // done
}
// scatter
tupleChan0 := make(chan voteResponseTuple, len(notYetResponded))
for id, peer := range notYetResponded {
go func(id uint64, peer Peer) {
resp, err := requestVoteTimeout(peer, r, 2*maximumElectionTimeout())
tupleChan0 <- voteResponseTuple{id, resp, err}
}(id, peer)
}
// gather
for i := 0; i < cap(tupleChan0); i++ {
select {
case t := <-tupleChan0:
if t.err != nil {
continue // will need to retry
}
respondedAlready[t.id] = nil // set membership semantics
tupleChan <- t
case <-abortChan:
return // give up
}
}
}
}()
return tupleChan, cancel(abortChan)
}
// 选举应答
type voteResponseTuple struct {
id uint64
response requestVoteResponse
err error
}
type canceler interface {
Cancel()
}
type cancel chan struct{}
func (c cancel) Cancel() { close(c) }
// 过滤peers
func disjoint(all, except peerMap) peerMap {
d := peerMap{}
for id, peer := range all {
if _, ok := except[id]; ok {
continue
}
d[id] = peer
}
return d
}
server.go
这是最重要的一个逻辑

节点配置变更
// 角色分类
const (
follower = "Follower"
candidate = "Candidate"
leader = "Leader"
)
const (
unknownLeader = 0
noVote = 0
)
// 选举时间随机范围[MinimumElectionTimeoutMS, maximumElectionTimeoutMS]
var (
MinimumElectionTimeoutMS int32 = 250
maximumElectionTimeoutMS = 2 * MinimumElectionTimeoutMS
)
var (
errNotLeader = errors.New("not the leader")
errUnknownLeader = errors.New("unknown leader")
errDeposed = errors.New("deposed during replication")
errAppendE#008000ntriesRejected = errors.New("appendEntries RPC rejected")
errReplicationFailed = errors.New("command replication failed (but will keep retrying)")
errOutOfSync = errors.New("out of sync")
errAlreadyRunning = errors.New("already running")
)
// 重置选举时间
func resetElectionTimeoutMS(newMin, newMax int) (int, int) {
oldMin := atomic.LoadInt32(&MinimumElectionTimeoutMS)
oldMax := atomic.LoadInt32(&maximumElectionTimeoutMS)
atomic.StoreInt32(&MinimumElectionTimeoutMS, int32(newMin))
atomic.StoreInt32(&maximumElectionTimeoutMS, int32(newMax))
return int(oldMin), int(oldMax)
}
// minimumElectionTimeout returns the current minimum election timeout.
func minimumElectionTimeout() time.Duration {
return time.Duration(MinimumElectionTimeoutMS) * time.Millisecond
}
// maximumElectionTimeout returns the current maximum election time.
func maximumElectionTimeout() time.Duration {
return time.Duration(maximumElectionTimeoutMS) * time.Millisecond
}
// 选举时间随机函数
func electionTimeout() time.Duration {
n := rand.Intn(int(maximumElectionTimeoutMS - MinimumElectionTimeoutMS))
d := int(MinimumElectionTimeoutMS) + n
return time.Duration(d) * time.Millisecond
}
// broadcastInterval returns the interval between heartbeats (AppendEntry RPCs)
// broadcast from the leader. It is the minimum election timeout / 10, as
// dictated by the spec: BroadcastInterval << ElectionTimeout << MTBF.
// 广播时间,用于Leader发送心跳广播,这个时间应小于选举时间;否则,非Leader节点会产生选举操作
func broadcastInterval() time.Duration {
d := MinimumElectionTimeoutMS / 10
return time.Duration(d) * time.Millisecond
}
// protectedString is just a string protected by a mutex.
type protectedString struct {
sync.RWMutex
value string
}
func (s *protectedString) Get() string {
s.RLock()
defer s.RUnlock()
return s.value
}
func (s *protectedString) Set(value string) {
s.Lock()
defer s.Unlock()
s.value = value
}
// protectedBool is just a bool protected by a mutex.
type protectedBool struct {
sync.RWMutex
value bool
}
func (s *protectedBool) Get() bool {
s.RLock()
defer s.RUnlock()
return s.value
}
func (s *protectedBool) Set(value bool) {
s.Lock()
defer s.Unlock()
s.value = value
}
// Server is the agent that performs all of the Raft protocol logic.
// In a typical application, each running process that wants to be part of
// the distributed state machine will contain a server component.
type Server struct {
id uint64 // id of this server
// 节点状态
state *protectedString
// 节点运行状态
running *protectedBool
// Leader节点标示
leader uint64
// 当前节点任期号
term uint64 // "current term number, which increases monotonically"
// 0表示,当前节点还有投出自己的票;
// 非零表示节点已经投票了,值是获票者的标示ID
vote uint64 // who we voted for this term, if applicable
log *raftLog
config *configuration
// 追加日志信道
appendEntriesChan chan appendEntriesTuple
// 投票信道
requestVoteChan chan requestVoteTuple
// 命令信道
commandChan chan commandTuple
// 配置修改信道
configurationChan chan configurationTuple
// 选举信道
electionTick <-chan time.Time
// 退出信道
quit chan chan struct{}
}
// 状态机函数
// 该函数不可并发执行,否则就达不到一致性状态机的效果(执行时间不要超过选举时间)
// 正常来说,只有"共识"达成的时候,才会调用该函数,然后返回给客户端
// 但是,在这里为了简化实现,"共识“算法是放在后台任务操作的,客户端发送命令单Leader时,Leader马上
// 应答客户端,并没有等”共识算法“的共识结果
type ApplyFunc func(commitIndex uint64, cmd []byte) []byte
// 初始化节点
// 1. 构建日志 2.初始化为"follower"角色 3.leader为"unknown"
func NewServer(id uint64, store io.ReadWriter, a ApplyFunc) *Server {
if id <= 0 {
panic("server id must be > 0")
}
// 5.2 Leader election: "the latest term this server has seen is persisted,
// and is initialized to 0 on first boot."
log := newRaftLog(store, a)
latestTerm := log.lastTerm()
s := &Server{
id: id,
state: &protectedString{value: follower}, // "when servers start up they begin as followers"
running: &protectedBool{value: false},
leader: unknownLeader, // unknown at startup
log: log,
term: latestTerm,
config: newConfiguration(peerMap{}),
appendEntriesChan: make(chan appendEntriesTuple),
requestVoteChan: make(chan requestVoteTuple),
commandChan: make(chan commandTuple),
configurationChan: make(chan configurationTuple),
electionTick: nil,
quit: make(chan chan struct{}),
}
s.resetElectionTimeout()
return s
}
type configurationTuple struct {
Peers []Peer
Err chan error
}
// 设置配置
// 1. 服务启动时,先设置配置
// 2. 集群变更时,设置配置
func (s *Server) SetConfiguration(peers ...Peer) error {
// 节点刚启动
if !s.running.Get() {
s.config.directSet(makePeerMap(peers...))
return nil
}
err := make(chan error)
// 节点已经启动了
s.configurationChan <- configurationTuple{peers, err}
return <-err
}
// Start triggers the server to begin communicating with its peers.
func (s *Server) Start() {
go s.loop()
}
// Stop terminates the server. Stopped servers should not be restarted.
func (s *Server) Stop() {
q := make(chan struct{})
s.quit <- q
<-q
s.logGeneric("server stopped")
}
// 命令元组
type commandTuple struct {
// 命令内容
Command []byte
// 命令信道
CommandResponse chan<- []byte
Err chan error
}
// 命令接口
func (s *Server) Command(cmd []byte, response chan<- []byte) error {
err := make(chan error)
s.commandChan <- commandTuple{cmd, response, err}
return <-err
}
// 日志追加
func (s *Server) appendEntries(ae appendEntries) appendEntriesResponse {
t := appendEntriesTuple{
Request: ae,
Response: make(chan appendEntriesResponse),
}
s.appendEntriesChan <- t
return <-t.Response
}
// 投票
func (s *Server) requestVote(rv requestVote) requestVoteResponse {
t := requestVoteTuple{
Request: rv,
Response: make(chan requestVoteResponse),
}
s.requestVoteChan <- t
return <-t.Response
}
// times out,
// new election
// | .-----.
// | | |
// v times out, | v receives votes from
// +----------+ starts election +-----------+ majority of servers +--------+
// | Follower |------------------>| Candidate |---------------------->| Leader |
// +----------+ +-----------+ +--------+
// ^ ^ | |
// | | discovers current leader | |
// | | or new term | |
// | '------------------------------' |
// | |
// | discovers server with higher term |
// '------------------------------------------------------------------'
//
//
func (s *Server) loop() {
s.running.Set(true)
for s.running.Get() {
switch state := s.state.Get(); state {
case follower:
s.followerSelect()
case candidate:
s.candidateSelect()
case leader:
s.leaderSelect()
default:
panic(fmt.Sprintf("unknown Server State '%s'", state))
}
}
}
func (s *Server) resetElectionTimeout() {
s.electionTick = time.NewTimer(electionTimeout()).C
}
func (s *Server) logGeneric(format string, args ...interface{}) {
prefix := fmt.Sprintf("id=%d term=%d state=%s: ", s.id, s.term, s.state.Get())
log.Printf(prefix+format, args...)
}
func (s *Server) logAppendEntriesResponse(req appendEntries, resp appendEntriesResponse, stepDown bool) {
s.logGeneric(
"got appendEntries, sz=%d leader=%d prevIndex/Term=%d/%d commitIndex=%d: responded with success=%v (reason='%s') stepDown=%v",
len(req.Entries),
req.LeaderID,
req.PrevLogIndex,
req.PrevLogTerm,
req.CommitIndex,
resp.Success,
resp.reason,
stepDown,
)
}
func (s *Server) logRequestVoteResponse(req requestVote, resp requestVoteResponse, stepDown bool) {
s.logGeneric(
"got RequestVote, candidate=%d: responded with granted=%v (reason='%s') stepDown=%v",
req.CandidateID,
resp.VoteGranted,
resp.reason,
stepDown,
)
}
func (s *Server) handleQuit(q chan struct{}) {
s.logGeneric("got quit signal")
s.running.Set(false)
close(q)
}
// 命令转发
// 如果当前节点不是Leader节点,并且已存在Leader节点,则其会以"代理“的角色,将命令转发至Leader节点
func (s *Server) forwardCommand(t commandTuple) {
switch s.leader {
case unknownLeader:
s.logGeneric("got command, but don't know leader")
t.Err <- errUnknownLeader
case s.id: // I am the leader
panic("impossible state in forwardCommand")
default:
leader, ok := s.config.get(s.leader)
if !ok {
panic("invalid state in peers")
}
s.logGeneric("got command, forwarding to leader (%d)", s.leader)
// We're blocking our {follower,candidate}Select function in the
// receive-command branch. If we continue to block while forwarding
// the command, the leader won't be able to get a response from us!
go func() { t.Err <- leader.callCommand(t.Command, t.CommandResponse) }()
}
}
// 配置变更
// 转发规则和命令转发一样
func (s *Server) forwardConfiguration(t configurationTuple) {
switch s.leader {
case unknownLeader:
s.logGeneric("got configuration, but don't know leader")
t.Err <- errUnknownLeader
case s.id: // I am the leader
panic("impossible state in forwardConfiguration")
default:
leader, ok := s.config.get(s.leader)
if !ok {
panic("invalid state in peers")
}
s.logGeneric("got configuration, forwarding to leader (%d)", s.leader)
go func() { t.Err <- leader.callSetConfiguration(t.Peers...) }()
}
}
// follower 节点逻辑
func (s *Server) followerSelect() {
for {
select {
case q := <-s.quit:
s.handleQuit(q)
return
// 命令转发
case t := <-s.commandChan:
s.forwardCommand(t)
// 集群变更转发
case t := <-s.configurationChan:
s.forwardConfiguration(t)
// Leader选举
case <-s.electionTick:
// 5.2 Leader election: "A follower increments its current term and
// transitions to candidate state."
if s.config == nil {
s.logGeneric("election timeout, but no configuration: ignoring")
s.resetElectionTimeout()
continue
}
s.logGeneric("election timeout, becoming candidate")
// 提高自己的任期号
s.term++
// 投票置为空
s.vote = noVote
// Leader
s.leader = unknownLeader
// 设置节点角色为"候选人"
s.state.Set(candidate)
// 重置选举时间,防止马上再次出发选举
s.resetElectionTimeout()
return
// 日志追加(除了客户端请求,leader的心跳也会出发这个行为)
case t := <-s.appendEntriesChan:
if s.leader == unknownLeader {
s.leader = t.Request.LeaderID
s.logGeneric("discovered Leader %d", s.leader)
}
// 处理日志最佳操作
resp, stepDown := s.handleAppendEntries(t.Request)
s.logAppendEntriesResponse(t.Request, resp, stepDown)
t.Response <- resp
// 如果节点已经脱离了当前的集群,需要跟新Leader地址
if stepDown {
// stepDown as a Follower means just to reset the leader
if s.leader != unknownLeader {
s.logGeneric("abandoning old leader=%d", s.leader)
}
s.logGeneric("following new leader=%d", t.Request.LeaderID)
s.leader = t.Request.LeaderID
}
// 选举
case t := <-s.requestVoteChan:
// 选举处理
resp, stepDown := s.handleRequestVote(t.Request)
s.logRequestVoteResponse(t.Request, resp, stepDown)
t.Response <- resp
// 如果落后于当前节点了,把当前的Leader修改为"unkownleader",等待讯据成功后,进行切换
if stepDown {
// stepDown as a Follower means just to reset the leader
if s.leader != unknownLeader {
s.logGeneric("abandoning old leader=%d", s.leader)
}
s.logGeneric("new leader unknown")
s.leader = unknownLeader
}
}
}
}
// 候选状态
func (s *Server) candidateSelect() {
if s.leader != unknownLeader {
panic("known leader when entering candidateSelect")
}
if s.vote != 0 {
panic("existing vote when entering candidateSelect")
}
// "[A server entering the candidate stage] issues requestVote RPCs in
// parallel to each of the other servers in the cluster. If the candidate
// receives no response for an RPC, it reissues the RPC repeatedly until a
// response arrives or the election concludes."
// 发起选举RPC
requestVoteResponses, canceler := s.config.allPeers().except(s.id).requestVotes(requestVote{
Term: s.term,
CandidateID: s.id,
LastLogIndex: s.log.lastIndex(),
LastLogTerm: s.log.lastTerm(),
})
defer canceler.Cancel()
// Set up vote tallies (plus, vote for myself)
votes := map[uint64]bool{s.id: true}
s.vote = s.id
s.logGeneric("term=%d election started (configuration state %s)", s.term, s.config.state)
// 如果已经达到了选举“共识”,则成功选举
if s.config.pass(votes) {
s.logGeneric("I immediately won the election")
s.leader = s.id
s.state.Set(leader)
s.vote = noVote
return
}
// "A candidate continues in this state until one of three things happens:
// (a) it wins the election, (b) another server establishes itself as
// leader, or (c) a period of time goes by with no winner."
for {
select {
case q := <-s.quit:
s.handleQuit(q)
return
// 命令转发
case t := <-s.commandChan:
s.forwardCommand(t)
// 配置更新转发,注意和Leader的不同
case t := <-s.configurationChan:
s.forwardConfiguration(t)
// 收到选举的应答
case t := <-requestVoteResponses:
s.logGeneric("got vote: id=%d term=%d granted=%v", t.id, t.response.Term, t.response.VoteGranted)
// "A candidate wins the election if it receives votes from a
// majority of servers in the full cluster for the same term."
// 本节点落后于其他几点
if t.response.Term > s.term {
s.logGeneric("got vote from future term (%d>%d); abandoning election", t.response.Term, s.term)
s.leader = unknownLeader
s.state.Set(follower)
s.vote = noVote
return // lose
}
// 收到了"落后"当前节点的应答,忽略掉它
if t.response.Term < s.term {
s.logGeneric("got vote from past term (%d<%d); ignoring", t.response.Term, s.term)
break
}
// 收到赞同票
if t.response.VoteGranted {
s.logGeneric("%d voted for me", t.id)
votes[t.id] = true
}
// "Once a candidate wins an election, it becomes leader."
// “共识”达成
if s.config.pass(votes) {
s.logGeneric("I won the election")
s.leader = s.id
s.state.Set(leader)
s.vote = noVote
return // win
}
// 收到日志追加(在这里,心跳也当做日志追加的方式发送)
case t := <-s.appendEntriesChan:
// "While waiting for votes, a candidate may receive an
// appendEntries RPC from another server claiming to be leader.
// If the leader's term (included in its RPC) is at least as
// large as the candidate's current term, then the candidate
// recognizes the leader as legitimate and steps down, meaning
// that it returns to follower state."
// 处理日志
resp, stepDown := s.handleAppendEntries(t.Request)
s.logAppendEntriesResponse(t.Request, resp, stepDown)
t.Response <- resp
// candidate节点落后于Leader节点
if stepDown {
s.logGeneric("after an appendEntries, stepping down to Follower (leader=%d)", t.Request.LeaderID)
s.leader = t.Request.LeaderID
s.state.Set(follower)
return // lose
}
// 虽然当前节点是candidate节点,但集群中此时可能存在多个candidate节点
case t := <-s.requestVoteChan:
// We can also be defeated by a more recent candidate
resp, stepDown := s.handleRequestVote(t.Request)
s.logRequestVoteResponse(t.Request, resp, stepDown)
t.Response <- resp
if stepDown {
// 当前candidate节点落后于集群中已存在的candidate节点,将自己的角色变为follower,
// 并且也会投赞同票
s.logGeneric("after a requestVote, stepping down to Follower (leader unknown)")
s.leader = unknownLeader
s.state.Set(follower)
return // lose
}
// 选举
case <-s.electionTick:
// "The third possible outcome is that a candidate neither wins nor
// loses the election: if many followers become candidates at the
// same time, votes could be split so that no candidate obtains a
// majority. When this happens, each candidate will start a new
// election by incrementing its term and initiating another round of
// requestVote RPCs."
s.logGeneric("election ended with no winner; incrementing term and trying again")
s.resetElectionTimeout()
s.term++
s.vote = noVote
return // draw
}
}
}
// Leader 保存的Follower节点的所有最新同步条目
type nextIndex struct {
sync.RWMutex
m map[uint64]uint64 // followerId: nextIndex
}
func newNextIndex(pm peerMap, defaultNextIndex uint64) *nextIndex {
ni := &nextIndex{
m: map[uint64]uint64{},
}
for id := range pm {
ni.m[id] = defaultNextIndex
}
return ni
}
// 找出已经同步Follower的最小日志
func (ni *nextIndex) bestIndex() uint64 {
ni.RLock()
defer ni.RUnlock()
if len(ni.m) <= 0 {
return 0
}
i := uint64(math.MaxUint64)
for _, nextIndex := range ni.m {
if nextIndex < i {
i = nextIndex
}
}
return i
}
// 返回节点(id)最新的同步日志
func (ni *nextIndex) prevLogIndex(id uint64) uint64 {
ni.RLock()
defer ni.RUnlock()
if _, ok := ni.m[id]; !ok {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("peer %d not found", id))
}
return ni.m[id]
}
// 自减节点(id)的最新同步日志,用于同步失败时的回滚
func (ni *nextIndex) decrement(id uint64, prev uint64) (uint64, error) {
ni.Lock()
defer ni.Unlock()
i, ok := ni.m[id]
if !ok {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("peer %d not found", id))
}
if i != prev {
return i, errOutOfSync
}
if i > 0 {
ni.m[id]--
}
return ni.m[id], nil
}
// 更新节点(id)的同步日志
func (ni *nextIndex) set(id, index, prev uint64) (uint64, error) {
ni.Lock()
defer ni.Unlock()
i, ok := ni.m[id]
if !ok {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("peer %d not found", id))
}
if i != prev {
return i, errOutOfSync
}
ni.m[id] = index
return index, nil
}
// 心跳、复制命令都会用到该函数,flush是同步的,如果对端节点不可达,则阻塞
func (s *Server) flush(peer Peer, ni *nextIndex) error {
peerID := peer.id()
// Leader的任期号
currentTerm := s.term
// 节点(peer)的最新同步索引
prevLogIndex := ni.prevLogIndex(peerID)
// 检索出peers节点落后于Leader几点的日志条目,然后进行同步
entries, prevLogTerm := s.log.entriesAfter(prevLogIndex)
// 获取Leader committed的最新索引
commitIndex := s.log.getCommitIndex()
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: term=%d leaderId=%d prevLogIndex/Term=%d/%d sz=%d commitIndex=%d", peerID, currentTerm, s.id, prevLogIndex, prevLogTerm, len(entries), commitIndex)
// 日志追加RPC
resp := peer.callAppendEntries(appendEntries{
Term: currentTerm,
LeaderID: s.id,
PrevLogIndex: prevLogIndex,
PrevLogTerm: prevLogTerm,
Entries: entries,
CommitIndex: commitIndex,
})
if resp.Term > currentTerm {
// 应答的节点比当前节点的任期号大,当前的Leader被罢免
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: responseTerm=%d > currentTerm=%d: deposed", peerID, resp.Term, currentTerm)
return errDeposed
}
if !resp.Success {
// 应答失败,可能是leader RPC等待超时,或者出现了网络错误(包括脑裂),回滚
newPrevLogIndex, err := ni.decrement(peerID, prevLogIndex)
if err != nil {
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: while decrementing prevLogIndex: %s", peerID, err)
return err
}
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: rejected; prevLogIndex(%d) becomes %d", peerID, peerID, newPrevLogIndex)
return errAppendEntriesRejected
}
if len(entries) > 0 {
// 复制成功,更新同步状态
newPrevLogIndex, err := ni.set(peer.id(), entries[len(entries)-1].Index, prevLogIndex)
if err != nil {
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: while moving prevLogIndex forward: %s", peerID, err)
return err
}
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: accepted; prevLogIndex(%d) becomes %d", peerID, peerID, newPrevLogIndex)
return nil
}
s.logGeneric("flush to %d: accepted; prevLogIndex(%d) remains %d", peerID, peerID, ni.prevLogIndex(peerID))
return nil
}
// Leader并发同步日志
func (s *Server) concurrentFlush(pm peerMap, ni *nextIndex, timeout time.Duration) (int, bool) {
type tuple struct {
id uint64
err error
}
responses := make(chan tuple, len(pm))
for _, peer := range pm {
go func(peer Peer) {
errChan := make(chan error, 1)
go func() { errChan <- s.flush(peer, ni) }()
go func() { time.Sleep(timeout); errChan <- errTimeout }()
responses <- tuple{peer.id(), <-errChan} // first responder wins
}(peer)
}
successes, stepDown := 0, false
for i := 0; i < cap(responses); i++ {
switch t := <-responses; t.err {
case nil:
s.logGeneric("concurrentFlush: peer %d: OK (prevLogIndex(%d)=%d)", t.id, t.id, ni.prevLogIndex(t.id))
successes++
case errDeposed:
// 当前的Leder节点落后于其他节点
s.logGeneric("concurrentFlush: peer %d: deposed!", t.id)
stepDown = true
default:
s.logGeneric("concurrentFlush: peer %d: %s (prevLogIndex(%d)=%d)", t.id, t.err, t.id, ni.prevLogIndex(t.id))
// nothing to do but log and continue
}
}
return successes, stepDown
}
// 作为Leader角色运行
func (s *Server) leaderSelect() {
if s.leader != s.id {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("leader (%d) not me (%d) when entering leaderSelect", s.leader, s.id))
}
if s.vote != 0 {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("vote (%d) not zero when entering leaderSelect", s.leader))
}
// 5.3 Log replication: "The leader maintains a nextIndex for each follower,
// which is the index of the next log entry the leader will send to that
// follower. When a leader first comes to power it initializes all nextIndex
// values to the index just after the last one in its log."
//
// I changed this from lastIndex+1 to simply lastIndex. Every initial
// communication from leader to follower was being rejected and we were
// doing the decrement. This was just annoying, except if you manage to
// sneak in a command before the first heartbeat. Then, it will never get
// properly replicated (it seemed).
// Leader为每个Follower保存了最新的同步日志索引
ni := newNextIndex(s.config.allPeers().except(s.id), s.log.lastIndex()) // +1)
flush := make(chan struct{})
heartbeat := time.NewTicker(broadcastInterval())
defer heartbeat.Stop()
go func() {
// 发送心跳,除了检测心跳外,还有防止Follower发送选举
for _ = range heartbeat.C {
flush <- struct{}{}
}
}()
for {
select {
case q := <-s.quit:
s.handleQuit(q)
return
// 收到命令
case t := <-s.commandChan:
// Append the command to our (leader) log
s.logGeneric("got command, appending")
currentTerm := s.term
entry := logEntry{
Index: s.log.lastIndex() + 1,
Term: currentTerm,
Command: t.Command,
commandResponse: t.CommandResponse,
}
// 追加日志
if err := s.log.appendEntry(entry); err != nil {
t.Err <- err
continue
}
s.logGeneric(
"after append, commitIndex=%d lastIndex=%d lastTerm=%d",
s.log.getCommitIndex(),
s.log.lastIndex(),
s.log.lastTerm(),
)
// Now that the entry is in the log, we can fall back to the
// normal flushing mechanism to attempt to replicate the entry
// and advance the commit index. We trigger a manual flush as a
// convenience, so our caller might get a response a bit sooner.
// 这里将日志同步放到了同步队列就返回给客户端了,正常来说,需要"共识"达成才返回给客户端
go func() { flush <- struct{}{} }()
t.Err <- nil
// 收到配置变更
case t := <-s.configurationChan:
// Attempt to change our local configuration
if err := s.config.changeTo(makePeerMap(t.Peers...)); err != nil {
t.Err <- err
continue
}
// Serialize the local (C_old,new) configuration
encodedConfiguration, err := s.config.encode()
if err != nil {
t.Err <- err
continue
}
// We're gonna write+replicate that config via log mechanisms.
// Prepare the on-commit callback.
entry := logEntry{
Index: s.log.lastIndex() + 1,
Term: s.term,
Command: encodedConfiguration,
isConfiguration: true,
committed: make(chan bool),
}
go func() {
// 当日志被commited时,committed将被回调
committed := <-entry.committed
if !committed {
s.config.changeAborted()
return
}
// 日志被committed了,说明其他节点都应用了最新的配置,所以当前的节点配置也需要更新
s.config.changeCommitted()
if _, ok := s.config.allPeers()[s.id]; !ok {
// 当前节点已被新集群剔除
s.logGeneric("leader expelled; shutting down")
q := make(chan struct{})
s.quit <- q
// 节点已退出
<-q
}
}()
// 日志追加
if err := s.log.appendEntry(entry); err != nil {
t.Err <- err
continue
}
case <-flush:
// 获取需要同步的节点
recipients := s.config.allPeers().except(s.id)
// Special case: network of 1
if len(recipients) <= 0 {
ourLastIndex := s.log.lastIndex()
if ourLastIndex > 0 {
if err := s.log.commitTo(ourLastIndex); err != nil {
s.logGeneric("commitTo(%d): %s", ourLastIndex, err)
continue
}
s.logGeneric("after commitTo(%d), commitIndex=%d", ourLastIndex, s.log.getCommitIndex())
}
continue
}
// Normal case: network of at-least-2
// 并发同步日志
successes, stepDown := s.concurrentFlush(recipients, ni, 2*broadcastInterval())
if stepDown {
// 节点已被卸任
s.logGeneric("deposed during flush")
s.state.Set(follower)
s.leader = unknownLeader
return
}
// Only when we know all followers accepted the flush can we
// consider incrementing commitIndex and pushing out another
// round of flushes.
if successes == len(recipients) {
// 最小被同步的Index
peersBestIndex := ni.bestIndex()
ourLastIndex := s.log.lastIndex()
ourCommitIndex := s.log.getCommitIndex()
if peersBestIndex > ourLastIndex {
// safety check: we've probably been deposed
s.logGeneric("peers' best index %d > our lastIndex %d", peersBestIndex, ourLastIndex)
s.logGeneric("this is crazy, I'm gonna become a follower")
s.leader = unknownLeader
s.vote = noVote
s.state.Set(follower)
return
}
if peersBestIndex > ourCommitIndex {
// committed Leader Index
if err := s.log.commitTo(peersBestIndex); err != nil {
s.logGeneric("commitTo(%d): %s", peersBestIndex, err)
// 比如某个Follower在同步Index时失败了,
continue // oh well, next time?
}
if s.log.getCommitIndex() > ourCommitIndex {
// 继续同步日志
s.logGeneric("after commitTo(%d), commitIndex=%d -- queueing another flush", peersBestIndex, s.log.getCommitIndex())
go func() { flush <- struct{}{} }()
}
}
}
// 追加日志, 正常来说,Leader节点是不会受到该命令的,出现这种的可能是集群存在一个新的Leader节点,这命令就是该Leader发送过来的
case t := <-s.appendEntriesChan:
resp, stepDown := s.handleAppendEntries(t.Request)
s.logAppendEntriesResponse(t.Request, resp, stepDown)
t.Response <- resp
if stepDown {
s.logGeneric("after an appendEntries, deposed to Follower (leader=%d)", t.Request.LeaderID)
s.leader = t.Request.LeaderID
s.state.Set(follower)
return // deposed
}
// 受到投票请求
case t := <-s.requestVoteChan:
resp, stepDown := s.handleRequestVote(t.Request)
s.logRequestVoteResponse(t.Request, resp, stepDown)
t.Response <- resp
if stepDown {
s.logGeneric("after a requestVote, deposed to Follower (leader unknown)")
s.leader = unknownLeader
s.state.Set(follower)
return // deposed
}
}
}
}
// handleRequestVote will modify s.term and s.vote, but nothing else.
// stepDown means you need to: s.leader=unknownLeader, s.state.Set(Follower).
// 处理投票
// 可能会修改s.term和s.vote 的值; stepDown意味着需要设置s.leader = unkownLeader, s.state.Set(Follower)
func (s *Server) handleRequestVote(rv requestVote) (requestVoteResponse, bool) {
// Spec is ambiguous here; basing this (loosely!) on benbjohnson's impl
// If the request is from an old term, reject
if rv.Term < s.term {
return requestVoteResponse{
Term: s.term,
VoteGranted: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf("Term %d < %d", rv.Term, s.term),
}, false
}
// If the request is from a newer term, reset our state
stepDown := false
if rv.Term > s.term {
// 本地节点落后于集群的其他节点,需要更新一下自己的任期号
s.logGeneric("requestVote from newer term (%d): we defer", rv.Term)
s.term = rv.Term
s.vote = noVote
s.leader = unknownLeader
stepDown = true
}
// Special case: if we're the leader, and we haven't been deposed by a more
// recent term, then we should always deny the vote
if s.state.Get() == leader && !stepDown {
// 如果本地节点是Leader,并且又不落后于req 节点,则投反对票
return requestVoteResponse{
Term: s.term,
VoteGranted: false,
reason: "already the leader",
}, stepDown
}
// If we've already voted for someone else this term, reject
// 如果已经投过票,则投失败票
if s.vote != 0 && s.vote != rv.CandidateID {
if stepDown {
panic("impossible state in handleRequestVote")
}
return requestVoteResponse{
Term: s.term,
VoteGranted: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf("already cast vote for %d", s.vote),
}, stepDown
}
// If the candidate log isn't at least as recent as ours, reject
if s.log.lastIndex() > rv.LastLogIndex || s.log.lastTerm() > rv.LastLogTerm {
return requestVoteResponse{
Term: s.term,
VoteGranted: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf(
"our index/term %d/%d > %d/%d",
s.log.lastIndex(),
s.log.lastTerm(),
rv.LastLogIndex,
rv.LastLogTerm,
),
}, stepDown
}
// We passed all the tests: cast vote in favor
s.vote = rv.CandidateID
s.resetElectionTimeout()
return requestVoteResponse{
Term: s.term,
VoteGranted: true,
}, stepDown
}
// handleAppendEntries will modify s.term and s.vote, but nothing else.
// stepDown means you need to: s.leader=r.LeaderID, s.state.Set(Follower).
// 追加日志,需要注意的是,handleAppendEntries也会修改s.term和s.vote
// stepDown也会修改s.Leader, s,state
// 需要注意的是,本地节点的state不同时,其行为也是不用的
func (s *Server) handleAppendEntries(r appendEntries) (appendEntriesResponse, bool) {
// Spec is ambiguous here; basing this on benbjohnson's impl
// Maybe a nicer way to handle this is to define explicit handler functions
// for each Server state. Then, we won't try to hide too much logic (i.e.
// too many protocol rules) in one code path.
// If the request is from an old term, reject
if r.Term < s.term {
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf("Term %d < %d", r.Term, s.term),
}, false
}
// If the request is from a newer term, reset our state
stepDown := false
if r.Term > s.term {
s.term = r.Term
s.vote = noVote
stepDown = true
}
// Special case for candidates: "While waiting for votes, a candidate may
// receive an appendEntries RPC from another server claiming to be leader.
// If the leader’s term (included in its RPC) is at least as large as the
// candidate’s current term, then the candidate recognizes the leader as
// legitimate and steps down, meaning that it returns to follower state."
if s.state.Get() == candidate && r.LeaderID != s.leader && r.Term >= s.term {
s.term = r.Term
s.vote = noVote
stepDown = true
}
// In any case, reset our election timeout
s.resetElectionTimeout()
// Reject if log doesn't contain a matching previous entry
// 如果{PreLogIndex, PreLogTerm} 不是最新的条目,则失败
// [{1, 2},{1, 3}, {1,4},{1,5},{1,6}] => {1,5} => [{1, 2},{1, 3}, {1,4},{1,5}]
if err := s.log.ensureLastIs(r.PrevLogIndex, r.PrevLogTerm); err != nil {
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf(
"while ensuring last log entry had index=%d term=%d: error: %s",
r.PrevLogIndex,
r.PrevLogTerm,
err,
),
}, stepDown
}
// Process the entries
for i, entry := range r.Entries {
// Configuration changes requre special preprocessing
var pm peerMap
// 处理配置
if entry.isConfiguration {
commandBuf := bytes.NewBuffer(entry.Command)
if err := gob.NewDecoder(commandBuf).Decode(&pm); err != nil {
panic("gob decode of peers failed")
}
if s.state.Get() == leader {
// TODO should we instead just ignore this entry?
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf(
"AppendEntry %d/%d failed (configuration): %s",
i+1,
len(r.Entries),
"Leader shouldn't receive configurations via appendEntries",
),
}, stepDown
}
// Expulsion recognition
if _, ok := pm[s.id]; !ok {
entry.committed = make(chan bool)
go func() {
if <-entry.committed {
s.logGeneric("non-leader expelled; shutting down")
q := make(chan struct{})
s.quit <- q
<-q
}
}()
}
}
// Append entry to the log
if err := s.log.appendEntry(entry); err != nil {
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf(
"AppendEntry %d/%d failed: %s",
i+1,
len(r.Entries),
err,
),
}, stepDown
}
// "Once a given server adds the new configuration entry to its log, it
// uses that configuration for all future decisions (it does not wait
// for the entry to become committed)."
if entry.isConfiguration {
if err := s.config.directSet(pm); err != nil {
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf(
"AppendEntry %d/%d failed (configuration): %s",
i+1,
len(r.Entries),
err,
),
}, stepDown
}
}
}
// Commit up to the commit index.
//
// < ptrb> ongardie: if the new leader sends a 0-entry appendEntries
// with lastIndex=5 commitIndex=4, to a follower that has lastIndex=5
// commitIndex=5 -- in my impl, this fails, because commitIndex is too
// small. shouldn't be?
// <@ongardie> ptrb: i don't think that should fail
// <@ongardie> there are 4 ways an appendEntries request can fail: (1)
// network drops packet (2) caller has stale term (3) would leave gap in
// the recipient's log (4) term of entry preceding the new entries doesn't
// match the term at the same index on the recipient
//
// 出现这种情况的原因可能是本地节点运行到committed逻辑的时候出现了问题,或者说应答给Leader时,网络出现了问题等等。
// 这些情况都会造成数据不同步的情况,也就是本地节点的commiitted情况和Leader节点保存的Follower(本地节点)不一致
if r.CommitIndex > 0 && r.CommitIndex > s.log.getCommitIndex() {
if err := s.log.commitTo(r.CommitIndex); err != nil {
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: false,
reason: fmt.Sprintf("CommitTo(%d) failed: %s", r.CommitIndex, err),
}, stepDown
}
}
// all good
return appendEntriesResponse{
Term: s.term,
Success: true,
}, stepDown
}
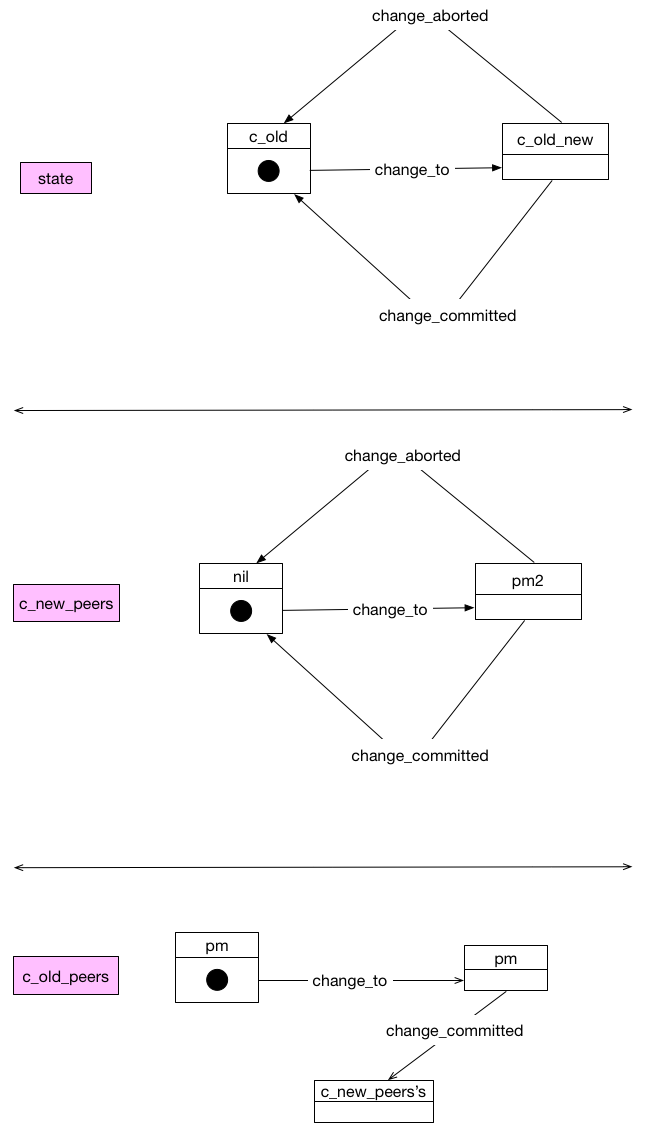
configuration.go
var (
errConfigurationAlreadyChanging = errors.New("configuration already changing")
)
const (
cOld = "C_old"
cOldNew = "C_old,new"
)
// configuration represents the sets of peers and behaviors required to
// implement joint-consensus.
type configuration struct {
sync.RWMutex
state string
// 老配置
cOldPeers peerMap
// 新配置-》用于过度
cNewPeers peerMap
}
// newConfiguration returns a new configuration in stable (C_old) state based
// on the passed peers.
func newConfiguration(pm peerMap) *configuration {
return &configuration{
state: cOld, // start in a stable state,
cOldPeers: pm, // with only C_old
}
}
// directSet is used when bootstrapping, and when receiving a replicated
// configuration from a leader. It directly sets the configuration to the
// passed peers. It's assumed this is called on a non-leader, and therefore
// requires no consistency dance.
// 配置变更
func (c *configuration) directSet(pm peerMap) error {
c.Lock()
defer c.Unlock()
c.cOldPeers = pm
c.cNewPeers = peerMap{}
c.state = cOld
return nil
}
func (c *configuration) get(id uint64) (Peer, bool) {
c.RLock()
defer c.RUnlock()
if peer, ok := c.cOldPeers[id]; ok {
return peer, true
}
if peer, ok := c.cNewPeers[id]; ok {
return peer, true
}
return nil, false
}
func (c *configuration) encode() ([]byte, error) {
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
if err := gob.NewEncoder(buf).Encode(c.allPeers()); err != nil {
return []byte{}, err
}
return buf.Bytes(), nil
}
// allPeers returns the union set of all peers in the configuration.
func (c *configuration) allPeers() peerMap {
c.RLock()
defer c.RUnlock()
union := peerMap{}
for id, peer := range c.cOldPeers {
union[id] = peer
}
for id, peer := range c.cNewPeers {
union[id] = peer
}
return union
}
// pass returns true if the votes represented by the votes map are sufficient
// to constitute a quorum. pass respects C_old,new requirements, which dictate
// that any request must receive a majority from both C_old and C_new to pass.
// 共识判断
func (c *configuration) pass(votes map[uint64]bool) bool {
c.RLock()
defer c.RUnlock()
// Count the votes
cOldHave, cOldRequired := 0, c.cOldPeers.quorum()
for id := range c.cOldPeers {
if votes[id] {
cOldHave++
}
if cOldHave >= cOldRequired {
break
}
}
// If we've already failed, we can stop here
if cOldHave < cOldRequired {
return false
}
// C_old passes: if we're in C_old, we pass
if c.state == cOld {
return true
}
// Not in C_old, so make sure we have some peers in C_new
if len(c.cNewPeers) <= 0 {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("configuration state '%s', but no C_new peers", c.state))
}
// Since we're in C_old,new, we need to also pass C_new to pass overall.
// It's important that we range through C_new and check our votes map, and
// not the other way around: if a server casts a vote but doesn't exist in
// a particular configuration, that vote should not be counted.
cNewHave, cNewRequired := 0, c.cNewPeers.quorum()
for id := range c.cNewPeers {
if votes[id] {
cNewHave++
}
if cNewHave >= cNewRequired {
break
}
}
return cNewHave >= cNewRequired
}
// 配置变更准备, prepare-change
func (c *configuration) changeTo(pm peerMap) error {
c.Lock()
defer c.Unlock()
if c.state != cOld {
return errConfigurationAlreadyChanging
}
if len(c.cNewPeers) > 0 {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("configuration ChangeTo in state '%s', but have C_new peers already", c.state))
}
c.cNewPeers = pm
c.state = cOldNew
return nil
}
// 提交变更逻辑
func (c *configuration) changeCommitted() {
c.Lock()
defer c.Unlock()
if c.state != cOldNew {
panic("configuration ChangeCommitted, but not in C_old,new")
}
if len(c.cNewPeers) <= 0 {
panic("configuration ChangeCommitted, but C_new peers are empty")
}
c.cOldPeers = c.cNewPeers
c.cNewPeers = peerMap{}
c.state = cOld
}
// 中断变更
func (c *configuration) changeAborted() {
c.Lock()
defer c.Unlock()
if c.state != cOldNew {
panic("configuration ChangeAborted, but not in C_old,new")
}
c.cNewPeers = peerMap{}
c.state = cOld
}
Demo
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"hash/fnv"
"net/http"
"net/url"
"time"
"github.com/peterbourgon/raft"
)
func main() {
a := func(idx uint64, cmd []byte) []byte {
fmt.Printf("%d, apply function: %s\n", idx, cmd)
return cmd
}
mustParseURL := func(rawURL string) *url.URL {
u, _ := url.Parse(rawURL)
u.Path = ""
return u
}
mustNewHTTPPeer := func(u *url.URL) raft.Peer {
p, err := raft.NewHTTPPeer(u)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return p
}
peersAddr := []string{
"127.0.0.1:7090",
"127.0.0.1:7091",
"127.0.0.1:7092",
"127.0.0.1:7093",
"127.0.0.1:7094"}
var ss []*raft.Server
for _, addr := range peersAddr {
hash := fnv.New64()
hash.Write([]byte(addr))
id := hash.Sum64()
hash.Reset()
s := raft.NewServer(id, &bytes.Buffer{}, a)
mux := http.NewServeMux()
raft.HTTPTransport(mux, s)
go func(addr string) {
if err := http.ListenAndServe(addr, mux); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}(addr)
ss = append(ss, s)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
for _, s := range ss {
s.SetConfiguration(
mustNewHTTPPeer(mustParseURL("http://127.0.0.1:7090")),
mustNewHTTPPeer(mustParseURL("http://127.0.0.1:7091")),
mustNewHTTPPeer(mustParseURL("http://127.0.0.1:7092")),
mustNewHTTPPeer(mustParseURL("http://127.0.0.1:7093")),
mustNewHTTPPeer(mustParseURL("http://127.0.0.1:7094")),
)
s.Start()
}
for {
cmd := []byte(time.Now().String())
cmdChan := make(chan []byte)
go ss[0].Command(cmd, cmdChan)
<-cmdChan
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500)
}
time.Sleep(time.Hour)
}
Run
» go run raft-server.go 2>/dev/null
1, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:13.668460404 +0800 CST
1, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:13.668460404 +0800 CST
1, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:13.668460404 +0800 CST
1, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:13.668460404 +0800 CST
1, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:13.668460404 +0800 CST
2, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.169165702 +0800 CST
2, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.169165702 +0800 CST
2, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.169165702 +0800 CST
2, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.169165702 +0800 CST
2, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.169165702 +0800 CST
3, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.670873193 +0800 CST
3, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.670873193 +0800 CST
3, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.670873193 +0800 CST
3, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.670873193 +0800 CST
3, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:14.670873193 +0800 CST
4, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.171741805 +0800 CST
4, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.171741805 +0800 CST
4, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.171741805 +0800 CST
4, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.171741805 +0800 CST
4, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.171741805 +0800 CST
5, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.673498401 +0800 CST
5, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.673498401 +0800 CST
5, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.673498401 +0800 CST
5, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.673498401 +0800 CST
5, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:15.673498401 +0800 CST
6, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:16.175658603 +0800 CST
6, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:16.175658603 +0800 CST
6, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:16.175658603 +0800 CST
6, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:16.175658603 +0800 CST
6, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:16.175658603 +0800 CST
7, apply function: 2017-09-11 11:41:16.677758823 +0800 CST